Declining birthrate is caused by increasing childlessness, and increasing childlessness is caused by the increase in those who have never married
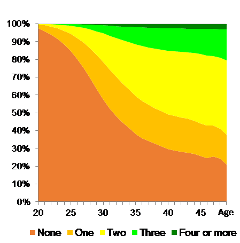
Figure 1: Number of children ever born by women’s age: 2014
Reference: The Human Fertility Database
(An international joint research project of over 30 countries led by the Max Planck Institute for Demographic Research)
It used to be said that “children are the nation’s treasure.” Today, many people are averse to such phrasing, but the children who will be born continue to represent Japan’s future, as they did in those days, and a society which does not produce future generations who form its foundation has no future.
According to the latest population projection released by the National Institute of Population and Social Security Research last year, Japan’s annual births are predicted to be 742,000 in 2040, and 557,000 in 2065, and 318,000 in 2115, one hundred years later from now. In this projection, too, the total decrease in births in the immediate five years from 2015 to 2020 is expected to be 100,000, which is significant. In annual average terms, this translates into a decrease of 20,000, so the actual annual decrease of 30,000 indicates that the drop in the number of births has started at a very rapid pace, and that if it stays at this pace, the aforementioned numerical predictions for the declining births must be moved up considerably.
First, let us consider the root cause of declining birthrate. See Figure 1. This graph shows the number of births by women’s age – the number of children women bore by each age. Of the women of reproductive age, the ages between 20 and 49, the percentage of those who are childless and have not had any children was as high as 47%. This data is from 2014, so today, in 2018, the proportion must be over 50%. In 1992, right before the Japanese government introduced measures to support couples in raising children, this figure was 35%, and childlessness was concentrated among those in their 20’s. Thus, for women in the ages between 30 and 49 years old, or in the prime of their child-rearing years, those who were childless accounted for only 15% at that time, but in 2014, this figure reached 33%. There is no data for men, but considering the gender gap in the proportion of the never-married population, today, childlessness among men between the ages of 20 and 49 is likely to be as high as a little over 60%, and approximately 50% for the ages between 30 and 49. An era where more than half of the reproductive population of both men and women are childless – an era of an increasingly childless society – has arrived.
This kind of continuous increase in the childless population has driven down the average number of children being born. So then, what is causing the increasing childlessness? As you know, it is the increase in the never-married population. In Japan, 98% of children are born to married couples, so marriage and birth are essentially synonymous. Therefore, when marriage declines and the proportion of the never-married population rises, fertility rates drops as a direct result. So then, what is causing the increase in the never-married population?
The hurdle of romantic marriage – a surge in never-married persons not in relationship with the opposite sex
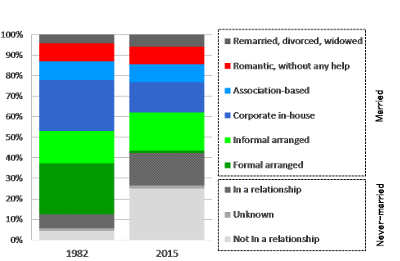
Figure 2: Partnerships of women aged 30
Reference: Akihiko Kato and Mariko Nakamura, “Weakening Community-Based Marriage and its Consequences, Part 2”. (A paper presented at the 27th Annual Meeting of the Japan Society of Family Sociology in 2017)
Using the statics from 2015, let us take a look at the partnerships (heterosexual relationships) between men and women in the age group of 25 to 29 (Japanese National Fertility Survey by the National Institute of Population and Social Security Research). First, for women, 39% of this age group are married, 26% are never-married but in a relationship (fiancé, boyfriend, male friend, etc.), and 34% are never-married and not in a relationship. Meanwhile, for men, 27% are married, 21% are never-married but in a relationship, and 50% are never-married and not in a relationship (the remaining 2% are unknown). In other words, when in their late 20s, when the search for a spouse or a boyfriend/girlfriend is at its peak, more than a third of women and more than a half of men were not in a relationship with the opposite sex.
But of course, in Japanese society, the youths lacking skills in love and romantic relationships is not news. Although marriage is said to have “changed from arranged marriage to love marriage” in the latter half of the 20th century, I pointed out that this understanding was not reflecting the reality of the increase in the never-married population correctly at the annual conference of the Japan Society of Family Sociology last year. Figure 2 is a graph which summarizes the main point of this argument. Here, the relationships women had when they were 30 years old in 1982 and 2015 are compared by the ways they met their partners, including those of women who were married.
As one can see in this graph, traditional marriage based on formal arranged matchmaking, where the parents of both parties meet face to face, has declined. (“Formal arranged” marriage in Figure 2 includes meeting through a marriage matchmaking agency.) However, the proportion of women who meet their partners and get married with the support of their friends, acquaintances and siblings has not declined. Additionally, there used to be many cases of such marriage as corporate in-house marriage, where the meeting took place at workplace and then led to marriage. The business executives of the Showa era in particular took getting their young employees to marry and form a family as part of their social responsibility to nurture them, and these business executives hired masses of young women (although they also expected the so-called “leaving the company for marriage”), and once employees started dating, the executives took it upon themselves to play the role of a ceremonial matchmaker (go-between). Today, there are fewer such companies and business executives, but marriage through meeting at the workplace still remains important; being second only to marriage through introduction. Marriage through association-based meetings, such as meeting partners at school and social clubs, has remained almost at the same level, and it has not been able to make up for the decline in marriage through meeting at the workplace.
Striking up a conversation with a stranger of the opposite sex around town, or during a trip, or at a part-time job, and developing a romantic relationship with that person, and eventually getting married, all without help from anyone, is the pattern of love marriage that has been the dream marriage for many Japanese, as it is free from social constraints. Interestingly, though, this type of marriage is in the minority, accounting for approximately 8% of all partnerships, and the proportion has not changed over time. On the other hand, when we turn our attention to the never-married, those not in a relationship have increased sharply from 5% to 25%. This proportion matches the decrease in formal arranged marriage (from 25% to 1%). The result suggests that the decline in formal arranged marriage has brought about the increase in never-married persons not in a relationship. As mentioned previously, men are in an even more serious situation. I will spare the details here, but will point out one thing: the generation not in a relationship with the opposite sex was born after the asset-inflated bubble economy, and most of their parents, whose marriages were love marriages according to them, were born in the 1960s. The time has come for us to let go of the illusion about love marriage.
Marriage and forming a family require “resources”

So, what kind of policies should be adopted? The answer is quite common sense-like. Basically, marriage and forming a family require money and help, but the younger generations of today lack both, so actively supplementing these things will be the main logic of such policies.
Of course, the principle is that the decision on marriage and giving birth is to be made by the person involved. One may choose not to have a family and stay single for life. However, according to the survey by the National Institute of Population and Social Security Research, even today, 90% of the never-married persons in their late 20s said they “intend to marry someday.” When asked what the biggest obstacle is, “money for marriage” came out as the top answer for both men and women, accounting for as much as 50%. In addition, couples who said the ideal number of children is three or more still account for about 40% of all couples, and not a few women had a mind to have a large family with multiple children. While not many women are able to have three or more children (see Figure 1), 70% of the couples stated the money issue as the reason for not being able to attain this ideal. Therefore, it is important to provide support in “resources” first.
Economists have estimated that raising one child would cost 20 to 30 million yen. As employment is becoming more unstable, it is very difficult to have a third child. If having a child is not possible due to financial burdens, measures to provide additional child allowances to households with multiple children and to low-income households can be considered. For instance, in rural areas, where living quarters are larger compared to urban areas, and where more child-rearing help is available from grandparents, relatives, neighbors and community-based childcare facilities, there are still people who believe that “children are treasures” as part of their familial values. However, employment is particularly unstable and income is lower in these rural areas, and thus, young people who cannot marry or give birth are increasing there. This is why expanding the cash benefits of child allowance to the level of income a mother may earn at a part-time job will enable an increase in marriage and birth, while also leading to regional revitalization. In fact, Germany is reported to be experiencing a baby boom currently, with its number of birth increasing, but it is the Muslim women who aspire to have a multiple children and are receiving generous child allowances (such as Syrian refugees) accounting for the majority of the increase. Such a baby boom is likely to be providing a positive influence on German women as well. Cash benefits always come under criticism, but policymakers should never forget the fact that public servants and employees of large companies have also been receiving child support allowance from their workplace in addition to the public child allowances. The key point of this policy is to guarantee the segment of young people, whose employment instability makes them ineligible to receive child support allowance from the workplace, the income that covers basic living expenses that is comparable to that of the elites and those with employment stability, by substantially expanding the public child allowances.
Face the reality of increasing childlessness and promote marriage support as a national movement

* The information contained herein is current as of May 2018.
* The contents of articles on Meiji.net are based on the personal ideas and opinions of the author and do not indicate the official opinion of Meiji University.
Information noted in the articles and videos, such as positions and affiliations, are current at the time of production.

